Threejs Materials#
If you haven’t seen my previous Threejs blog post. I recommend reading that to get a better understanding on the topic. Three.js *Three.js is a popular open-source JavaScript library used for creating and displaying 3D computer graphics in a web…*medium.com
Let’s start with basic material first.
LineBasicMaterial#
LineBasicMaterial is a type of material that is used to render lines in a 3D scene. It is a simple material that does not have any lighting or shading effects and renders each line segment as a constant color.
// Don't think of this plane for now we will discuss it later
//extra code starts from here
let planeGeo = new PlaneGeometry(100, 100);
let planeMat = new MeshPhongMaterial({
color: "gray",
side: DoubleSide,
});
let plane = new Mesh(planeGeo, planeMat);
plane.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
scene.add(plane);
//extra code ends here
let points = [new Vector3(0, 0, 0), new Vector3(0, 10, 0)];
let lineGeo = new BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(points);
let lineMat = new LineBasicMaterial({
color: "white",
linewidth: 1,
});
let line = new Line(lineGeo, lineMat);
scene.add(line);
// extra code
let light = new AmbientLight("white", 1);
light.position.set(0, 10, 0);
scene.add(light);
camera.position.set(70, 50, 0);
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
LineDashedMaterial#
LineDashedMaterial is a type of material that is used to render dashed lines in a 3D scene. Here is an example of how to use LineDashedMaterial
Note: for using LineDashMaterial line.computeLineDistances() is must
computeLineDistances method is called on the Line object to compute the line distances for dashed rendering. This method calculates the distance between each pair of vertices in the LineGeometry and stores them in an array, which is used by the LineDashedMaterial to render the dashes.
// Don't think of this plane for now we will discuss it later
//extra code starts from here
let planeGeo = new PlaneGeometry(100, 100);
let planeMat = new MeshPhongMaterial({
color: "gray",
side: DoubleSide,
});
let plane = new Mesh(planeGeo, planeMat);
plane.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
scene.add(plane);
//extra code ends here
let points = [new Vector3(0, 0, 0), new Vector3(0, 10, 0)];
let lineGeo = new BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(points);
const material = new LineDashedMaterial({
color: 0xffffff,
linewidth: 1,
scale: 1,
dashSize: 3,
gapSize: 1,
});
let line = new Line(lineGeo, material);
line.computeLineDistances();
scene.add(line);
let light = new AmbientLight("white", 1);
light.position.set(0, 10, 0);
scene.add(light);
camera.position.set(70, 50, 0);
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
Now Let’s use little more usefull material
MeshBasicMaterial#
MeshBasicMaterial is a type of material that is used to render meshes in a 3D scene. It is a simple material that does not have any lighting or shading effects and renders each mesh face with a constant color or texture. Here is an example of how to use MeshBasicMaterial in Three.js:
// Don't think of this plane for now we will discuss it later
//extra code starts from here
let planeGeo = new PlaneGeometry(100, 100);
let planeMat = new MeshPhongMaterial({
color: "gray",
side: DoubleSide,
});
let plane = new Mesh(planeGeo, planeMat);
plane.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
scene.add(plane);
//extra code ends here
let boxGeo = new BoxGeometry(10, 10, 10);
let boxMat = new MeshBasicMaterial({
color: "red",
});
let box = new Mesh(boxGeo, boxMat);
scene.add(box);
let light = new AmbientLight("white", 1);
light.position.set(0, 10, 0);
scene.add(light);
camera.position.set(70, 50, 0);
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();

At first glance, it doesnot not resemble a box. Because MeshBasicMaterial doesnot interact with light or shading while rendering.
Use this interactive tool for better understanding of MeshBasicMaterial Three.js Material Browser Edit descriptionthreejs.org
MeshLambertMaterial#
MeshLambertMaterial is a type of material in Three.js that is used to create a surface that appears to have a matte finish, with no specular highlights. It takes various properties such as color, emissive, map, lightMap, opacity, etc. Here’s an example of how to use MeshLambertMaterial:
// Add a plane to provide some context
const planeGeo = new PlaneGeometry(100, 100);
const planeMat = new MeshPhongMaterial({
color: "gray",
side: DoubleSide,
});
const plane = new Mesh(planeGeo, planeMat);
plane.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
plane.position.set(0, -10, 0);
scene.add(plane);
// Add some lights to the scene
const ambientLight = new AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.5);
scene.add(ambientLight);
const pointLight = new PointLight(0xffffff, 0.5, 0);
pointLight.position.set(150, 100, 100);
scene.add(pointLight);
let boxGeo = new BoxGeometry(10, 10, 10);
let boxMat = new MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x049ef4,
});
box = new Mesh(boxGeo, boxMat);
scene.add(box);
// Set up camera position and update projection matrix
camera.position.set(50, 50, 50);
camera.lookAt(scene.position);
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
Use this interactive tool for better understanding Three.js Material Browser Edit descriptionthreejs.org
MeshPhongMaterial#
MeshPhongMaterial is a type of material that allows you to define the appearance of a 3D object based on the interaction of light sources in the scene. Here’s an example of how to use MeshPhongMaterial:
// Add a plane to provide some context
const planeGeo = new PlaneGeometry(100, 100);
const planeMat = new MeshPhongMaterial({
color: "gray",
side: DoubleSide,
});
const plane = new Mesh(planeGeo, planeMat);
plane.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
plane.position.set(0, -10, 0);
scene.add(plane);
// Add some lights to the scene
const ambientLight = new AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.5);
scene.add(ambientLight);
const pointLight = new PointLight(0xffffff, 0.5, 0);
pointLight.position.set(150, 100, 100);
scene.add(pointLight);
let boxGeo = new BoxGeometry(10, 10, 10);
let boxMat = new MeshPhongMaterial({
color: 0x049ef4,
});
box = new Mesh(boxGeo, boxMat);
scene.add(box);
// Set up camera position and update projection matrix
camera.position.set(50, 50, 50);
camera.lookAt(scene.position);
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();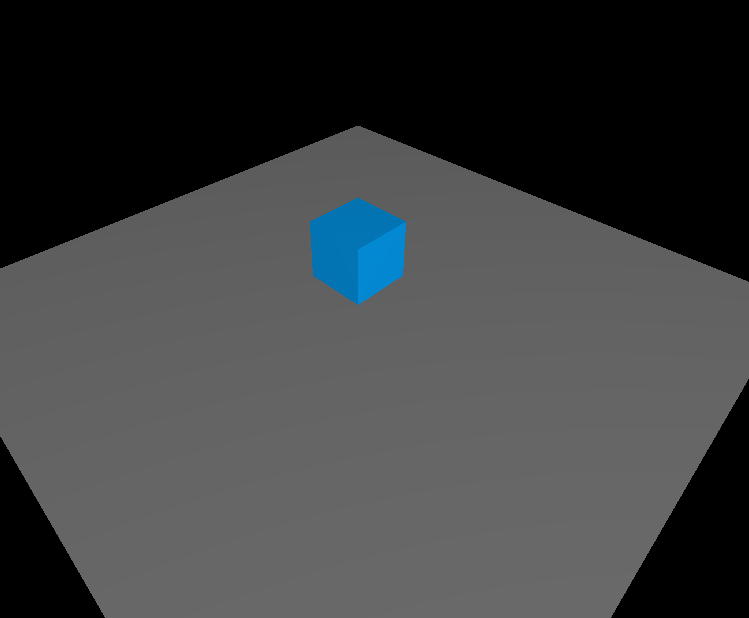
Use this interactive tool for better understanding Three.js Material Browser Edit descriptionthreejs.org
Now these are very usefull and advanced material so you should be very practical
MeshPhysicalMaterial#
MeshPhysicalMaterial is a physically based material in Three.js, which simulates how light interacts with real-world materials. It supports a variety of properties such as metallicness, roughness, and clearcoat.
-
Clearcoat: Some materials — like car paints, carbon fiber, and wet surfaces — require a clear, reflective layer on top of another layer that may be irregular or rough. Clearcoat approximates this effect, without the need for a separate transparent surface.
-
Physically-based transparency: One limitation of .opacity is that highly transparent materials are less reflective. Physically-based .transmission provides a more realistic option for thin, transparent surfaces like glass.
-
Advanced reflectivity: More flexible reflectivity for non-metallic materials.
-
Sheen: Can be used for representing cloth and fabric materials.
It is best to test yourself because it is very useful threejs webgl - materials - hdr environment mapping Edit descriptionthreejs.org

MeshStandardMaterial#
A standard physically based material, using Metallic-Roughness workflow.
Physically based rendering (PBR) has recently become the standard in many 3D applications, such as Unity, Unreal and 3D Studio Max.
Now these are very usefull and advanced material so you should be very practical Three.js Material Browser > Edit descriptionthreejs.org
MeshToonMaterial#
A material implementing toon shading.
Use this interactive tool for better understanding
Now these are very usefull and advanced material so you should be very practical Three.js Material Browser > Edit descriptionthreejs.org

MeshDepthMaterial#
MeshDepthMaterial is a type of material that is used to render the depth of a mesh in a 3D scene. This material renders a mesh using its depth information, which is the distance between each point of the mesh and the camera, as a grayscale value.
Use this interactive tool for better understanding Three.js Material Browser Edit descriptionthreejs.org
If you have any queries, feel free to contact us on https://discord.gg/RDU62RrFe3